Home » Product Line » Moisture Retention Curve Systems – Update Draft

SoilMoisture’s MC Lab Setups are the main (direct) method for creating Soil Moisture Retention Curve. SoilMoisture Lab Setups are capable of processing tens of samples at the same time with minimal sample preparation.
Our durable lab setups are designed to work with massive numbers of soil samples every day. With minimal maintenance or repair, they’ll last for a lifetime. That is why SoilMoisture Lab Setups are almost always the preferred systems in commercial soil labs, research institutes, and universities.
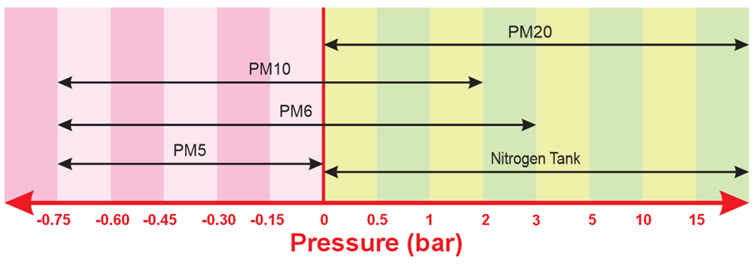
The range of pressure application is the main factor for selecting the right MC Lab Setup.

Part Number | Reference Number | Specifications | User Manual | Image | Quantity | Add to cart | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
LAB03V1 | Moisture Retention Curve System, 5 bar Application Range, 110V |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Moisture Retention Curve System, 5 bar Application Range, 110V | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
LAB03V2 | Moisture Retention Curve System, 5 bar Application Range, 220V |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Moisture Retention Curve System, 5 bar Application Range, 220V | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
MC5-N | Moisture Retention Curve System, 5 bar Application Range, Less Compressor |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Moisture Retention Curve System, 5 bar Application Range, Less Compressor | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
LAB02V1 | Moisture Retention Curve System, Complete, 15 bar Application Range, 110V |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Moisture Retention Curve System, Complete, 15 bar Application Range, 110V | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
LAB02V2 | Moisture Retention Curve System, Complete, 15 bar Application Range, 220V |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Moisture Retention Curve System, Complete, 15 bar Application Range, 220V | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
MC15-N | Moisture Retention Curve System, 15 bar Application Range, Less Compressor |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Moisture Retention Curve System, 15 bar Application Range, Less Compressor | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
LAB023V1 | Moisture Retention Curve System, 5 bar and 15 bar Application Range, 110V |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Moisture Retention Curve System, 5 bar and 15 bar Application Range, 110V | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
LAB023V2 | Moisture Retention Curve System, 5 bar and 15 bar Application Range, 220V |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Moisture Retention Curve System, 5 bar and 15 bar Application Range, 220V | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
YLAB023 | Moisture Retention Curve System, 5 bar and 15 bar Application Range, Less Compressor |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Moisture Retention Curve System, 5 bar and 15 bar Application Range, Less Compressor | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1768B-.15SYS3 | Moisture Retention Curve System, 3x Sandbox Tension Tables, 0 to 15 cbar Vacuum Range, Shelf is Not Included |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Moisture Retention Curve System, 3x Sandbox Tension Tables, 0 to 15 cbar Vacuum Range, Shelf is Not Included | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
LAB09G4 | Moisture Retention Curve System, Ceramic Tension Table, 0 to 75 cbar Vacuum Range |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Moisture Retention Curve System, Ceramic Tension Table, 0 to 75 cbar Vacuum Range | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
LAB1425F1 | Moisture Retention Curve System, 5X TM5 Tempe Cell Setup, 2 bar Application Range |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Moisture Retention Curve System, 5X TM5 Tempe Cell Setup, 2 bar Application Range | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Part Number | Reference Number | Specifications | User Manual | Image | Quantity | Add to cart | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1600F1 | SB5, Pressure Vessel, 5 bar Application Range, Rust resistant (Water+) |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Used in/with: SB5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1500F2 | SB15, Pressure Vessel, 15 bar Application Range, Rust Resistant (Water+), Less 1080G1 Hinge |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Used in/with: SB15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PV15 | SB15, Pressure Vessel, 15 bar Application Range, Rust Resistant (Water+), Including 1080G1 Hing |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Used in/with: SB15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0700G5 | Precision Pressure Stabilizer Manifold, 1 bar Application Range, Non-Relieving |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Precision Pressure Stabilizer Manifold, 1 bar Application Range, Non-Relieving | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0700G6 | TM5, Precision Pressure Stabilizer Manifold, 2 bar Application Range, Non-Relieving |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Used in/with: TM5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0700G3F1 | PV5, Pressure Stabilizer Manifold, 5 bar Application Range |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Used in/with: PV5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0700G2 | PV15, Pressure Stabilizer Manifold, 15 bar Application Range |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Used in/with: PV15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0725G2 | Precision Vacuum Stabilizer Manifold, -34 cbar Application Range |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Precision Vacuum Stabilizer Manifold, -34 cbar Application Range | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0725G1 | MCT75, Precision Vacuum Stabilizer Manifold, -100 cbar Application Range |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Used in/with: MCT75 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0500F1G3 | MC5/15, Heavy Duty Air Compressor, 20 bar, 110V |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Used in/with: MC5, MC15, MC5N15
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0500F1G4 | MC5/15, Heavy Duty Air Compressor, 20 bar, 220V |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Used in/with: MC5, MC15, MC5N15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2008F2 | MC2/MCT, Automated Pressure/Vacuum Pump, -1 to +10 bar, 110V |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Used in/with: MC2, MCT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0675B0 | Extraction Plate, Zero Tension, for Sandbox Tension Table, used with 325 Mesh Sand (SKU 932-10) |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Used in/with: MCT15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0675B0.5M2 | Extraction Plate, Ceramic Type FB (0.5 bar Application Range) |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Extraction Plate, Ceramic Type FB (0.5 bar Application Range) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0675B01M1 | Extraction Plate, Ceramic Type: Type 1B (1 bar Application Range) |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Extraction Plate, Ceramic Type: Type 1B (1 bar Application Range) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0675B01M3 | Extraction Plate, Ceramic Type 1HB (1 bar Application Range, High Flow) |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Used in/with: MC5, MC15, MC5N15, MCT75 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0675B02M1 | Extraction Plate, Ceramic Type 2B (2 bar Application Range) |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Extraction Plate, Ceramic Type 2B (2 bar Application Range) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0675B03M1 | Extraction Plate, Ceramic Type 3B (3 bar Application Range) |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Used in/with: MC5, MC15, MC5N15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0675B05M1 | Extraction Plate, Ceramic Type 5B (5 bar Application Range) |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Used in/with: MC5, MC15, MC5N15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0675B15M1 | Extraction Plate, Ceramic Type 15B (15 bar Application Range) |  | Max: Min: 1 Step: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More Info Used in/with: MC5, MC15, MC5N15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Developing soil moisture retention curve is at the core of soil hydrology studies that aim to understand the soil-water dynamics, such as recharge processes, enhance hydrological models used in climate studies, carbon respiration and sequestration processes, soil-plant-atmospheric systems, and more.
SoilMoisture’s MC Lab Setups are the main (direct) and the most accurate method for creating the Soil Moisture Retention Curve.
Our MC Lab Setups are designed to work with massive numbers of soil samples every day. With minimal maintenance or repair, they’ll last for a lifetime. That is why SoilMoisture Lab Setups are almost always the preferred systems in commercial soil labs, research institutes, and universities.
The range of pressure application is the main factor for selecting the right MC Lab Setup.
A soil moisture retention curve (also called the soil water retention curve or soil water characteristic curve or soil moisture release curve) is a graph that shows the relationship between the soil water content and the soil water potential (or matric potential). It describes how tightly water is held in the soil and how much water is available to plants or for other applications at a certain level of soil wetness.
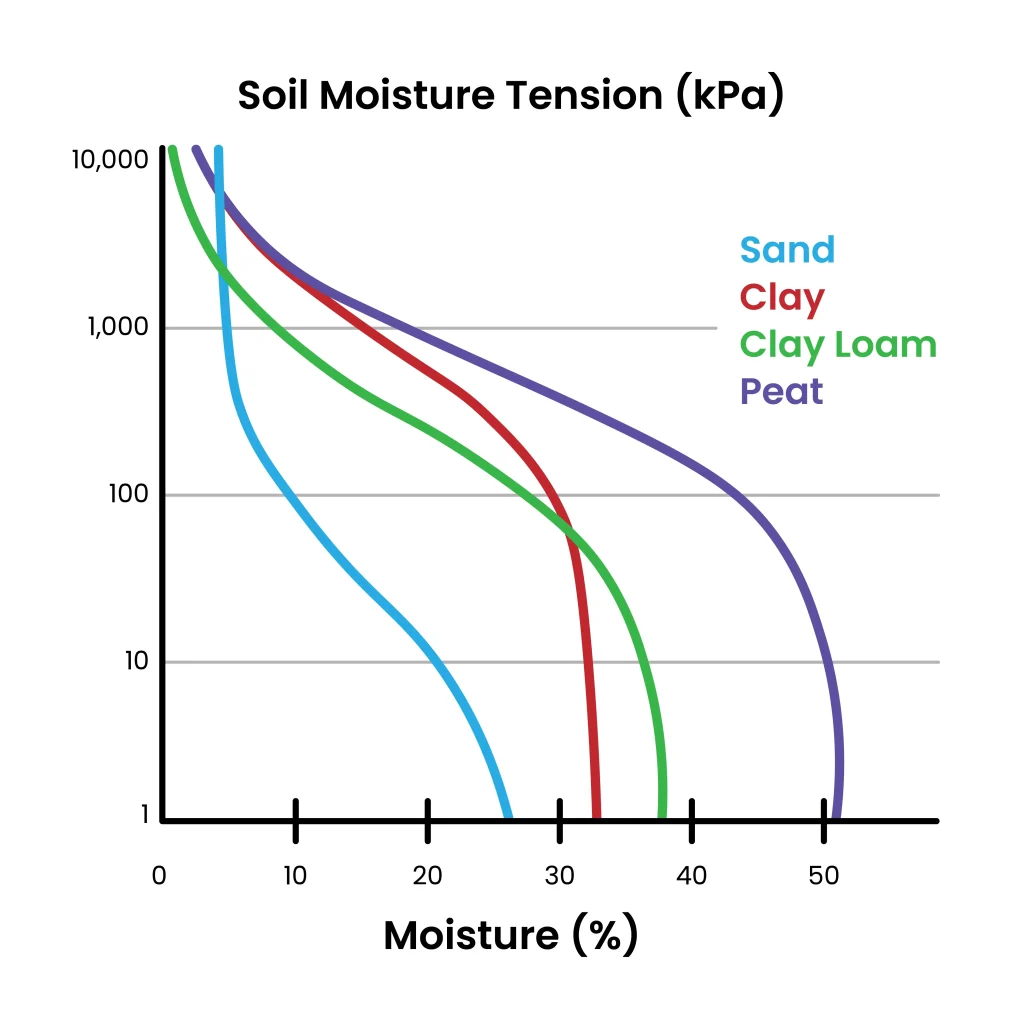
Soil Water Content (Y-axis): Can be volumetric or gravimetric. This tells you how much water is present in the soil.
Soil water potential (X-axis): Usually measured in negative pressure units (e.g., kPa or bars), representing the tension (pressure, suction, energy) needed to extract water from the soil. The more negative, the drier and harder it is to extract the water.
| pF | Water Potential (hPa cm H₂O) | Water Potential (kPa) | Water Potential (bar) | Typical Soil Condition |
| 0 | 1 | −0.1 | 0.001 | Saturated (near free water) |
| 1 | 10 | −1 | 0.01 | Very wet |
| 2 | 100 | −10 | 0.1 | Near saturation |
| 2.5 | 316 | −31.6 | 0.33 | Field capacity |
| 3 | 1,000 | −100 | 1 | Plant-available water zone |
| 4 | 10,000 | −1000 | 10 | Drying soil |
| 4.2 | 15,000 | −1500 | 15 | Permanent wilting point |
| 5 | 100,000 | −10,000 | 100 | Oven-dry soil / hygroscopic water |
Components of Soil Water Potential:
Matric potential (Ψm): | Due to adhesion and capillarity between water and soil particles. Dominant in unsaturated soils. |
Gravitational potential (Ψg): | Due to the height of water above a reference level. Important for water movement in saturated zones. |
Osmotic potential (Ψo): | Caused by solutes (e.g., salts) in soil water. Important for plant uptake but doesn’t affect water flow in the soil. |
Pressure potential (Ψp): | Positive in saturated soils under waterhead pressure |
 Soil Water Content (% of water in the soil) on the Y-axis of a graph is the most widely used format in soil physics, agronomy, and hydrology. It makes sense functionally it shows how water content responds to increasing soil tension. The curve slopes downward, showing less water content as tension (suction) increases.
Soil Water Content (% of water in the soil) on the Y-axis of a graph is the most widely used format in soil physics, agronomy, and hydrology. It makes sense functionally it shows how water content responds to increasing soil tension. The curve slopes downward, showing less water content as tension (suction) increases.
However, there are graphs where the Soil Water Content is displayed on the X-axis and used in engineering or specific modeling contexts where water content is the independent variable. This curve slopes downward as well, but water potential becomes more negative with decreasing water content.
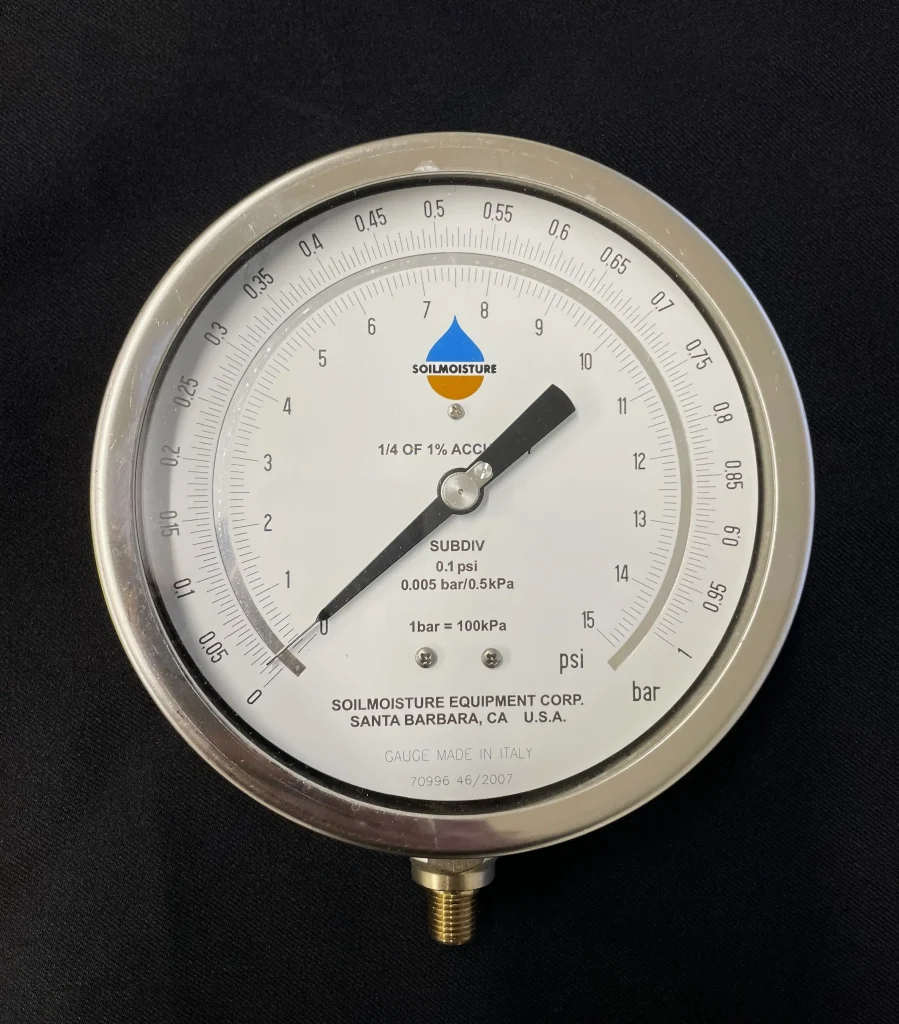
This SoilMoisture graph presents kPa as a positive value because the SoilMoisture system is placing positive pressure on the soil samples to push the water out. The inverse of this value is the negative pressure that represents the tension, pressure, suction needed to extract (pull) the water from the soil.
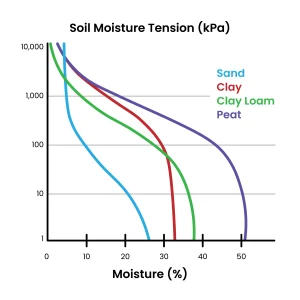
Important Points on the Curve:

Soil Condition | Approx. Potential (kPa) |
Saturation | 0 |
Field Capacity (FC) | −10 to −33 |
Plant Available Range | FC to −1500 |
Permanent Wilting Point | −1500 |
Oven dry | < −10,000 |

The soil moisture retention curve is determined through laboratory or field measurements that relate soil water content to soil water potential.
Here’s how it’s typically done:
Method of collecting soil sample | Tool / Type | Best for | Pros |
Auger Sampling | Hand auger or powered auger. Bucket auger, screw auger, tube auger. | Collecting soil at various depths. | Good for deep profiles and undisturbed cores. |
Core Sampling (Soil Cores) | Soil corer (manual or hydraulic). | Collecting undisturbed cylindrical samples for lab analysis (e.g., bulk density, retention curves). | Maintains soil structure; essential for physical property testing. |
Shovel or Spade Sampling | Shovel, spade, or trowel. | Surface or shallow soil layers. | Simple and cost-effective. |
Probe Sampling | Soil probe (hollow metal rod with a handle). | Quick, uniform sampling for fertility testing. | Easy to use and good for composite samples.
Limited depth and doesn’t retain structure. |
Pit Sampling | Digging a soil pit (manually or with backhoe). | Detailed soil profile studies. | Visual assessment of horizons, structure, and roots. |
Composite Sampling | Mix multiple subsamples from a defined area. | Average nutrient or contamination levels. | Avoid edges, pathways, and abnormal spots for accurate representation. |
Grid or Zone Sampling (for precision agriculture) | Probes, augers, GPS. | Large fields and variable-rate fertilizer applications. | Use GPS-guided grid or management zones. |
The sample is subjected to a series of decreasing soil water potentials, and water content is measured at each stage.
Common methods (Both provided by SoilMoisture Equipment Corp):
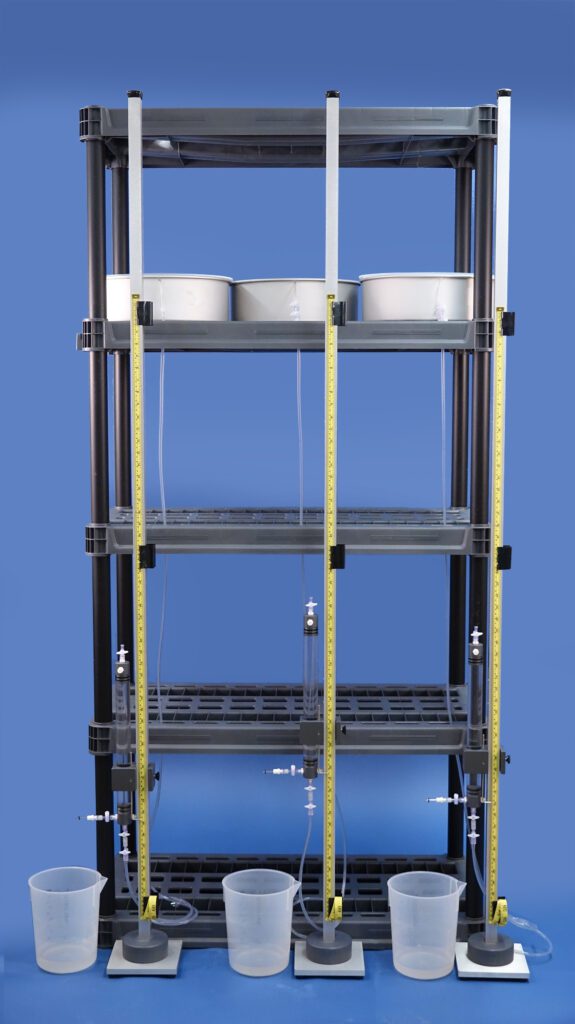
a. Tension Table / Hanging Water Column (0 to ~−30 kPa)


The SoilMoisture tension Lab Setup consists of a Sandbox Tension Table connected to a hanging Water Column. The height difference between the surface of the saturated sand (shown in yellow) and the dripping port of the Hanging Water Column determines the tension level applied.
b. Pressure Plate Apparatus (-30 to -1500 kPa)


Left: Main components of a Pressure system, including a source for pressured air, a pressure regulator and stabilizer, and a pressure vessel. Right: soil sample (shown in brown) is placed over a Porous Ceramic Plate (yellow) inside a Pressure Vessel (Blue). Pressurized air inside the Pressure Vessel drives water out of the soil sample into the Porous Ceramic Plate and eventually out of the Pressure Vessel.

Vacuum method (left) vs Pressure Method (right). In the Vacuum Method, the sample is placed over a Tension Table (made of sand, ceramic, glass bid, etc.). Vacuum is applied to the Tension Table extracts water out of the soil sample. In the Pressure Method, the soil sample is placed over a porous ceramic plate inside a Pressure Vessel. Pressurized Air inside of the Pressure Vessel drives water out of the soil sample, through the ceramic plate, and eventually out of the extractor.










Half-bar Ceramic (CF): High temperature fire, Alumina body, highly porous, high permeability, high flow rate, high mechanical strength, white color, inert surface area, very low ionic exchange capacity. Suitable for tension tables, soil water sampling under low tension (50 kPa and lower).
One Bar Ceramic (C1): Moderate temperature fire, largely Talc body, high porosity, good mechanical strength, ivory white, Suitable for low-range tensiometers, extraction plates, tension tables. Some ionic exchange capacity, not suitable for soil water samplers (chemical analysis of water samples).
One Bar High Flow Ceramic (C1H): High temperature fire, Alumina body, highly porous, high permeability, high flow rate, high mechanical strength, white color, inert surface area, very low ionic exchange capacity. Suitable for extraction plates, tension tables, soil water samplers, and tensiometers.
Two Bar Ceramic (C2): Moderate temperature fire, ball clay body, good porosity, good hydraulic conductivity, white color, suitable for extraction plates.
Two Bar High Flow Ceramic (C2H): High temperature fire, Silica body (porcelain), good porosity, good hydraulic conductivity, white color, very low ionic exchange capacity, inert surface area, suitable for soil water sampling.
Three Bar Ceramic (C3): Moderate temperature fire, ball clay body, good porosity, good infiltration rate, moderate mechanical strength, hard tannish-white color, suitable for extraction plates.
Five Bar ceramic (C5): Moderate temperature fire, ball clay body, low porosity, low infiltration rate, moderate mechanical strength, hard brownish-white color, suitable for extraction plates.
Fifteen bar Ceramic (C15): Moderate temperature fire, ball clay body, low porosity, low infiltration rate, moderate mechanical strength, hard pinkish tan color, suitable for extraction plates.
Custom-Made Ceramic Items:
Since SoilMoisture ceramics are unique in the world, the company manufactures 1000s of custom-made ceramic items for researchers and manufacturers worldwide each year.
Please consider the following items when ordering a custom-made ceramic item.
+ Review Standard Options: Before asking for a custom-made ceramic item (which will be more costly compared to a similar standard item), review all our standard ceramic items to see if any of them works for your application.
+ Drawing: If needed, provide us with the drawing of the custom-made item. Drawing is not required for simple shapes like a round plate, a square plate, a cylinder, etc.
+ Dimensions: Make sure to include all the dimensions required to make the ceramic item.
+ Tolerances: This is a critical piece of information that many overlook and fail to provide. Please note that we will be unable to provide you with an item price or manufacture an item unless all the dimensions are provided with their associated tolerances. Our ‘regular’ tolerance is +/-0.020 inches. Tighter tolerances are more costly.
+ Ceramic type: SoilMoisture manufactures 8 types of porous ceramic (CF, C1, C1H, C2, C2H, C3, C5, and C15). You need to choose a ceramic type for your custom-made order. Please note that SoilMoisture does not provide other types of ceramics. In other words, we do not custom-make ceramic types.
+ Quantity: SoilMoisture does not usually offer a price break for quantities lower than 500 units. Nevertheless, the quantity is needed for generating an official price quote.







Measuring the soil moisture retention curve matters because it provides critical insight into how water behaves in soil, which directly impacts agriculture, hydrology, and environmental management. The retention curve shows how much water soil holds, when the soil releases it, and how accessible the water in the soil is to plants and processes—making it a cornerstone of both agronomic and environmental science. Here’s why it’s important:
A. Determines Plant-Available Water
B. Supports Efficient Irrigation
C. Improves Soil and Water Management
D. Inputs for Hydrological and Climate Models
E. Soil Health, Land Slides, and Engineering
F. Environmental and Stormwater Monitoring
